Unveiling the Chemical Bonding Crossword Puzzle Answers: Embark on an intriguing journey into the captivating realm of chemical bonding, where the intricate interplay of atoms and molecules takes center stage. Prepare to unravel the secrets of ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds, deciphering the clues that lead to a deeper understanding of the molecular world.
As we delve into the crossword puzzle answers, we’ll uncover the fundamental principles that govern chemical bonding, shedding light on the forces that shape the structures and properties of matter. Get ready to witness the fascinating dance of electrons, protons, and neutrons as they form the building blocks of our universe.
Chemical Bonding
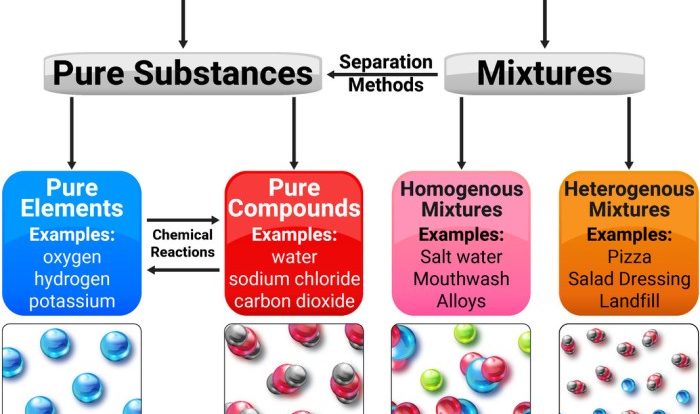
Chemical bonding refers to the attractive forces that hold atoms or ions together to form chemical substances. These forces arise due to the interactions between the electrons and nuclei of the atoms involved.There are three main types of chemical bonding: ionic, covalent, and metallic.
Ionic bonding occurs when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another, resulting in the formation of oppositely charged ions. Covalent bonding involves the sharing of electrons between atoms, forming a covalent bond. Metallic bonding occurs when electrons are delocalized over a metal lattice, creating a sea of mobile electrons.
Ionic Bonding, Chemical bonding crossword puzzle answers
Ionic bonding is a type of chemical bond formed between atoms of metals and non-metals. In ionic bonding, one or more electrons are transferred from the metal atom to the non-metal atom, resulting in the formation of positively charged metal ions and negatively charged non-metal ions.
The oppositely charged ions are attracted to each other by electrostatic forces, forming an ionic bond.Examples of ionic compounds include sodium chloride (NaCl), potassium chloride (KCl), and calcium oxide (CaO).
Covalent Bonding
Covalent bonding is a type of chemical bond formed between atoms of non-metals. In covalent bonding, the atoms share one or more pairs of electrons, forming a covalent bond. The shared electrons are attracted to the nuclei of both atoms, forming a strong bond.Examples
of covalent compounds include hydrogen gas (H2), methane (CH4), and water (H2O).
Metallic Bonding
Metallic bonding is a type of chemical bond formed between atoms of metals. In metallic bonding, the metal atoms share their valence electrons, forming a sea of mobile electrons. The positive metal ions are attracted to the sea of electrons, forming a strong bond.Examples
of metallic compounds include sodium (Na), potassium (K), and aluminum (Al).
FAQ Overview: Chemical Bonding Crossword Puzzle Answers
What is the significance of chemical bonding?
Chemical bonding is the driving force behind the formation of molecules and compounds, determining their properties and shaping the behavior of matter.
How do different types of chemical bonding affect molecular properties?
Ionic bonds result in the formation of charged species, covalent bonds create shared electron pairs, and metallic bonds give rise to a sea of delocalized electrons, each influencing molecular stability, reactivity, and physical characteristics.
What are some real-world applications of chemical bonding?
Chemical bonding principles underpin a vast array of applications, from the development of new materials and pharmaceuticals to the understanding of biological processes and the harnessing of energy.