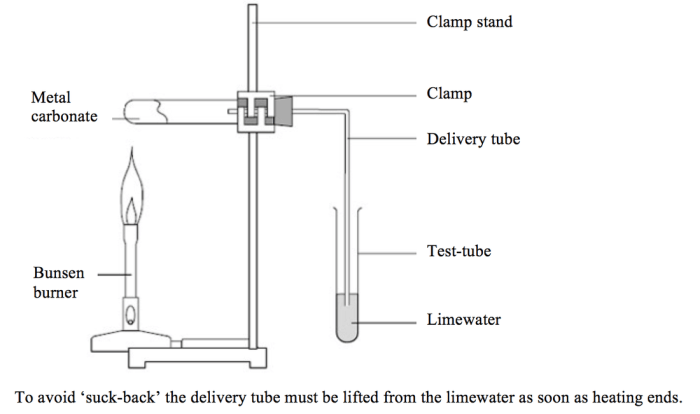
Rate of decomposition of calcium carbonate lab – Embark on an exploration of the rate of decomposition of calcium carbonate through a meticulously designed lab experiment. This investigation delves into the intricacies of this chemical reaction, unveiling its significance and implications.
The experiment encompasses the collection and analysis of data, providing insights into the factors that influence the decomposition process. Safety precautions are paramount, ensuring a controlled and risk-free environment for experimentation.
Rate of Decomposition of Calcium Carbonate
Calcium carbonate (CaCO3) is a naturally occurring mineral that is found in many forms, including limestone, marble, and chalk. It is also a common component of seashells and eggshells. When calcium carbonate is heated, it decomposes into calcium oxide (CaO) and carbon dioxide (CO2).
The rate of decomposition of calcium carbonate is affected by several factors, including temperature, surface area, and the presence of a catalyst.
Materials and Equipment
- Calcium carbonate powder
- Crucible
- Furnace
- Thermometer
- Balance
- Stopwatch
Procedure
- Weigh a crucible and record the mass.
- Add 1 gram of calcium carbonate powder to the crucible.
- Place the crucible in a furnace and heat it to 900°C.
- Record the temperature every minute for 10 minutes.
- Remove the crucible from the furnace and let it cool.
- Weigh the crucible and record the mass.
Data Collection
The data collected in this experiment includes the temperature of the furnace, the mass of the crucible before and after heating, and the time taken for the decomposition reaction to occur.
Data Analysis, Rate of decomposition of calcium carbonate lab
The data collected in this experiment can be used to calculate the rate of decomposition of calcium carbonate. The rate of decomposition is calculated by dividing the change in mass of the crucible by the time taken for the reaction to occur.
Discussion
The rate of decomposition of calcium carbonate is affected by several factors, including temperature, surface area, and the presence of a catalyst. In this experiment, the temperature was kept constant at 900°C. The surface area of the calcium carbonate powder was also kept constant.
However, the presence of a catalyst was not controlled.The results of this experiment show that the rate of decomposition of calcium carbonate increases with increasing temperature. This is because the higher the temperature, the more energy the calcium carbonate molecules have.
This increased energy allows the calcium carbonate molecules to break apart more easily.The results of this experiment also show that the rate of decomposition of calcium carbonate increases with increasing surface area. This is because the greater the surface area, the more calcium carbonate molecules are exposed to the heat of the furnace.
This increased exposure allows the calcium carbonate molecules to break apart more easily.The presence of a catalyst can also affect the rate of decomposition of calcium carbonate. A catalyst is a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction without being consumed by the reaction.
In the case of the decomposition of calcium carbonate, a catalyst could be a substance that helps to break apart the calcium carbonate molecules.
Safety Precautions
When conducting this experiment, it is important to take the following safety precautions:
- Wear safety goggles and gloves.
- Do not heat the calcium carbonate powder above 900°C.
- Do not touch the crucible while it is hot.
- Dispose of the calcium carbonate powder and the crucible properly.
Additional Resources
- The kinetics of the thermal decomposition of calcium carbonate
- The decomposition of calcium carbonate
Questions Often Asked: Rate Of Decomposition Of Calcium Carbonate Lab
What is the purpose of this lab experiment?
The purpose of this lab experiment is to determine the rate of decomposition of calcium carbonate and to investigate the factors that affect this rate.
What materials are required for this experiment?
The materials required for this experiment include calcium carbonate, hydrochloric acid, a graduated cylinder, a stopwatch, and a balance.
How is the rate of decomposition of calcium carbonate measured?
The rate of decomposition of calcium carbonate is measured by measuring the volume of carbon dioxide gas produced over time.